Open topic with navigation
Extensible Markup Language (XML) defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. XML is often used to exchange data over the Internet.
You can use the Database Setup wizard to convert hierarchical XML files to a flat database table in which each row represents a record of data and each column represents a field. The topics in this section describe how the structure of your XML file influences the fields and records that result from this conversion. They also describe the options in the Database Setup wizard that you can use to configure your database for use as a for your BarTender .
As with text, JSON, and files, the XML file or embedded sample data that you provide in the wizard is considered to be a sample file that is replaced with a different file during automated printing. Therefore, the file or embedded sample data should contain examples of all elements and attributes that are likely to appear in the XML files that you will use for printing. The database schema (column names) is created from these attribute and element nodes. If a node is missing, a corresponding column (field) name is not created for it.
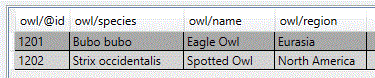
The following example illustrates how a simple XML file is converted to a flat database table.
The sample XML file is as follows.

When you connect BarTender to the XML file by using the Database Setup wizard, the XML is converted to the following database table.
In This Section
-
XML Structure Overview
Learn about the various structural components of an XML file and how they are converted to database records, fields, and data.
-
Database Setup Wizard Options
The Database Setup wizard offers functionality and options that you can use to define how the XML should be interpreted when it is converted to a database.
-
Using Aliases
Learn how to create aliases to use instead of the long field names that often result from an XML file.
 Example
Example

